Hearing Loss & Fall Risk: Improving Balance in the Aged Care Market
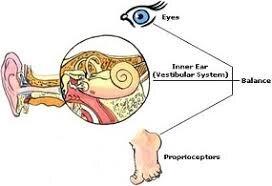
Balanced mobility is a complex process that involves three major components: proprioception, vision, and the vestibular system. The brain receives input from each system to identify external surroundings and determine the safest course of movement within that environment.
Compromising a single component can reduce the quality of balance as a whole as the components are integrated to form a single sensorimotor system.
Symptoms of Balance Disorders
Sufferers of balance disorders are unable to adapt their movements according to the environment. They might not be able to detect a change in terrain - i.e. from grassy fields to sand, often feeling disoriented as a result. In severe cases, sufferers are constantly affronted by episodes of dizziness, vertigo, blurred vision, confusion, fainting spells and a constant struggle with the perception of nearby objects. This may lead to problems such as bumping into others or increased risks of falling - which remains the leading cause of injury-related death in adults.
In most cases, sufferers of balance disorders undergo symptoms regardless of their position, whether they’re standing, walking or lying down.
UNDERSTANDING THE VESTIBULAR SYSTEM
The ears are a multi-functional organ, enabling us to process sound signals from our immediate environments, and serving as the seat of the vestibular system, a crucial component of balance.
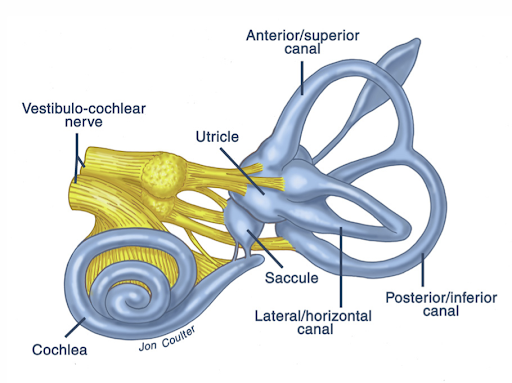
Our vestibular system in the inner ear system that processes balance input through equilibrium, motion, and spatial orientation. The system consists of the vestibule and three semicircular canals in each ear.
The saccule and utricle, known collectively as the vestibule, are membranous sacs that detect (otolith) and motion via linear orientation. Inner surfaces of vestibules feature sensory cells known as the macula, which coordinates head position relative to a vertical axis. They’re situated beneath the semicircular canals. Additionally, the vestibule comprises small crystals known as otoliths, which detect acceleration. This enables us to detect the speed while on a moving train or the drop of an elevator.
Semicircular canals are associated with detecting rotatory movements. These semicircular canals taper off into space (ampullae) covered with small sensory hair cells. The ampullae and canals are filled with a liquid known as endolymph. The endolymph undergoes inertia whenever we turn our heads toward a specific direction, which stimulates the sensory hairs that send nerve impulses to the brain that signal a change in course.
Each semicircular canal is responsible for a different type of head rotations: tilting up/down, tilting left/right, and turning sideways.
Optimal vestibular systems are meant to simultaneously transmit nervous signals from both ears to regulate stable motion. Unfortunately, injuries, aging, and various medical conditions may lead to hearing loss, which disrupts the natural functions of the vestibular system and affects balance.
***
It is important to note that although hearing loss may affect balance, this isn’t always necessarily the case. To clarify this, we can say that only hearing loss related to parts of the inner ear involved in the vestibular system is responsible for the impaired balance. So be sure to check with your healthcare advisor to determine the affected areas of your hearing condition.
***
Common Causes of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss may be conductive or sensorineural, depending on the cause of the condition. Conductive hearing loss is treatable and usually resolved through natural recovery, medicine or surgery. Sufferers don’t require extensive long-term devices such as hearing aids.
Common causes of conductive hearing loss include:
1. Ear infections such as otitis media, which blocks the fluid of your middle ears.
2. The thick wax build-up that obstructs ear canals. These are to be treated by professionals.
3. Head trauma resulting from injury - this may result in long-term hearing loss, best to sort the details with your primary healthcare provider.
Sensorineural hearing loss is linked to balance disorders as they affect the sensory components of inner ear structures. Unlike conductive hearing loss, sensorineural cases are untreatable and require specialized care and devices such as hearing aids. The loss of hearing may occur gradually, on its own or accompanying signs of tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
Common causes of sensorineural hearing loss include:
1. Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease (AIED) - a rare and serious condition that causes rapid hearing loss. The condition occurs when the immune system of sufferers mistakenly attacks inner ear structures.
2. Deafening Noise - extremely loud sounds can cause permanent damage to hearing components. These include exposure to fireworks, rock concerts, and gunfire.
3. Presbycusis - the gradual weakening of ear structures with age. This leads to an inability to hear speech clearly, which interferes with daily communication.
Diagnosing Hearing Loss
A hearing specialist can officially diagnose the severity of hearing loss with the application of an audiogram test. The healthy hearing range is between 0-20 decibels (with slight differences that come with age). Profound hearing loss applies to anything beyond 90 decibels. Audiologists will also be able to perform other tests, such as physical examinations, to determine if a hearing loss is conductive, sensorineural, or a combination of both.
Through prompt diagnosis, audiologists will be able to prescribe the best treatment and therapy to prevent the progression of hearing loss and reduce symptoms.
Coping with Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a potentially depressing condition. Sufferers will find it more challenging to integrate with society, and live out their daily life. This may even lead to complications such as balance disorders and elevated blood pressure due to stress.
Hearing Aids - These compact devices are worn by sufferers of sensorineural hearing loss. They're used to adjusting soundwaves so damaged/weakened parts of the inner ear can perceive sounds as they normally would. Modern hearing aids now come equipped with a plethora of features, which include a connection to mobile applications that personalizes volume control.
Cochlear Implants - a surgical procedure for more serious hearing conditions. The implants bypass the damaged or non-functional sensory parts of the ear to directly interact with hearing nerves that facilitate brain signals.
Improving Balance with Hearing Loss
Balance involves three components. By strengthening the other aspects of balance (proprioception and vision) sufferers of sensorineural hearing loss can better cope with their balance disorders.
To enhance the proprioceptive side of balance and stability we can look at the role of textured insoles. Naboso Technology offers revolutionary textured products to enhance sensation of the feet thereby improving balance. Their product line includes insoles, mats, and flooring.
Additional ways to improve proprioceptive input includes:
- whole body vibration such as Power Plate
- Holding a textured ball in the hand or using a product such as Smovey
- Kinesiology tape such as RockTape
To learn more about improving balance through sensory input please check out our past blog HERE